需求背景
最近项目基于springboot做微信机器人,从网上看了一下,一般都是单个用户登录,然后一个线程死循环,类似监听器,如果有信息就处理信息。但是,我们的要求是需要可以多个用户登录,所以,每次登录一个用户,开启一个线程,用户意外退出或者接口响应错误的情况下,该线程回收。
具体流程图如下:
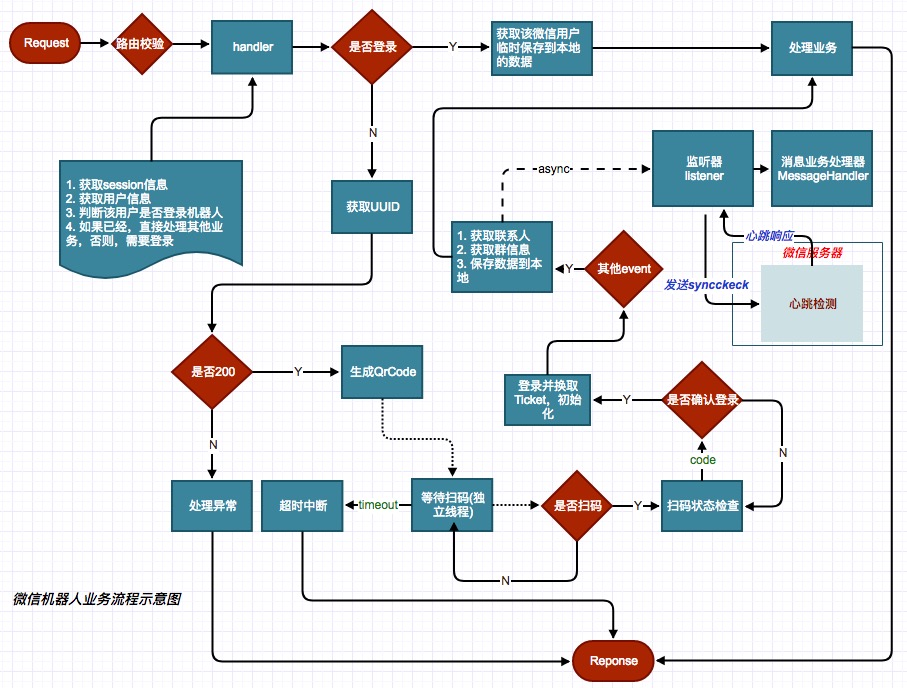
设计思路很简单,但是问题真多。具体遇到的问题,在另一篇中详细讲解吧。此处,就想解决线程池争取资源时间太长的问题,想放弃前面的思路,直接在项目启动的时候开启一个监听器线程,循环处理。也就是上面流程图中async的监听器,原来是每个登录请求都会创建,现在设计为程序启动后直接开启一个线程监听,从队列中获取信息,新来的机器人加入到队列末尾,依次遍历,同微信服务器保持心跳。虽然两者都有很多弊端,能支持4-8个机器人同时在线即可。
开启线程
方法1
首先想到方法是在Application的main方法中创建一个线程:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty("https.protocols", "TLSv1");
System.setProperty("jsse.enableSNIExtension", "false");
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(WxbotApplication.class);
application.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.CONSOLE);
application.addListeners(new PropertiesListener("classpath*:*.properties"));
application.run(args);
Thread listener = new Thread(new RobotListenJob());
listener.start();
}
|
但是如果我的RobotListenJob里面有些service需要注入的时候,这时候,虽然spring给我留了接口可获取容器中的bean,但是不太优雅,甚至是有些部署环境还会无法启动该线程,如果是单独的jar包服务,方法1和方法2均是可行的,但是web中不一定可行。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public class RobotListenJob implements Runnable {
private WxbotService wxbotService;
public RobotListenJob() {
wxbotService = getWxbotService();
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (wxbotService != null) {
wxbotService.listen();
}
}
private WxbotService getWxbotService() {
return SpringContextUtils.getBean(WxbotService.class);
}
}
|
这种方式,可能就是wxbotService对象还没有实例化,同样还有一种就是在Application中获取wxbotService实例,传给RobotListenJob的构造函数,代码如方法2。
方法2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty("https.protocols", "TLSv1");
System.setProperty("jsse.enableSNIExtension", "false");
ApplicationContext ctx = SpringApplication.run(WxbotApplication.class, args);
Thread listener = new Thread(new RobotListenJob(ctx.getBean(WxbotService.class)));
listener.start();
}
|
RobotListenJob增加有参构造函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class RobotListenJob implements Runnable {
private WxbotService wxbotService;
public RobotListenJob(WxbotService wxbotService) {
this.wxbotService = wxbotService;
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (wxbotService != null) {
wxbotService.listen();
}
}
}
|
上述方法1和方法2,如果你的web项目继承了SpringBootServletInitializer,且在protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder)该方法中构建了Application.class,是没有问题的,如下。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public class SpringBootStartApplication extends SpringBootServletInitializer {
@Override
protected SpringApplicationBuilder configure(SpringApplicationBuilder builder) {
return builder.sources(WxbotApplication.class);
}
}
|
方法3
下面我们看看终极大招一,使用@Component的注解方式来开启一个线程,还是利用了spring注解的原理以及spring初始化bean的方式(无参构造器),其他没什么新意。直接通过构造函数,开启一个线程。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
@Component
public class RobotListenJob implements DisposableBean, Runnable {
@Resource
private WxbotService wxbotService;
private Thread thread;
public RobotListenJob() {
thread = new Thread(this);
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (wxbotService != null) {
wxbotService.listen();
}
}
@Override
public void destroy(){
}
}
|
方法4
springboot启动过程产生的6种事件,包括ApplicationStartingEvent、ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent、ApplicationPreparedEvent、ApplicationStartedEvent、ApplicationReadyEvent、``和ApplicationFailedEvent,通过ApplicationReadyEvent事件可以实现系统启动完后做一些系统初始化的操作。
- ApplicationStartingEvent: springboot应用启动且未作任何处理(除listener注册和初始化)的时候发送ApplicationStartingEvent
- ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent: 确定springboot应用使用的Environment且context创建之前发送这个事件
- ApplicationPreparedEvent: context已经创建且没有refresh发送个事件
- ApplicationStartedEvent: context已经refresh且application and command-line runners(如果有) 调用之前发送这个事件
- ApplicationReadyEvent: application and command-line runners (如果有)执行完后发送这个事件,此时应用已经启动完毕
- ApplicationFailedEvent: 应用启动失败后产生这个事件
创建RoboJobListener事件监听器,实现onApplicationEvent方法,在ApplicationReadyEvent就绪时,调用WxbotService服务。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| public class RoboJobListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent>{
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationStartingEvent){
return;
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent){
return;
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent){
return;
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationStartedEvent){
return;
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationReadyEvent){
ApplicationContext context = ((ApplicationReadyEvent) event).getApplicationContext();
WxbotService wxbotService = context.getBean(WxbotService.class);
wxbotService.listen();
return;
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationFailedEvent){
return;
}
}
}
|
注册监听器listener,在SpringApplication初始化的时候添加进去。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| @SpringBootApplication
public class WxbotApplication {
public static void main(String[]args){
new SpringApplicationBuilder().sources(WxbotApplication.class)
.listeners(new RoboJobListener()).run(args);
}
}
|
方法5
除了springboot启动过程产生的6种事件中通过ApplicationReadyEvent事件可以实现系统启动完后做一些系统初始化的操作外,springboot应用还可以通过ApplicationRunner(CommandLineRunner也类似)这种方式也可以实现同样的功能。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| @Component
public class RobotListenJob implements ApplicationRunner {
@Resource
private WxbotService wxbotService;
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
if (wxbotService != null) {
wxbotService.listen();
}
});
thread.start();
}
}
|